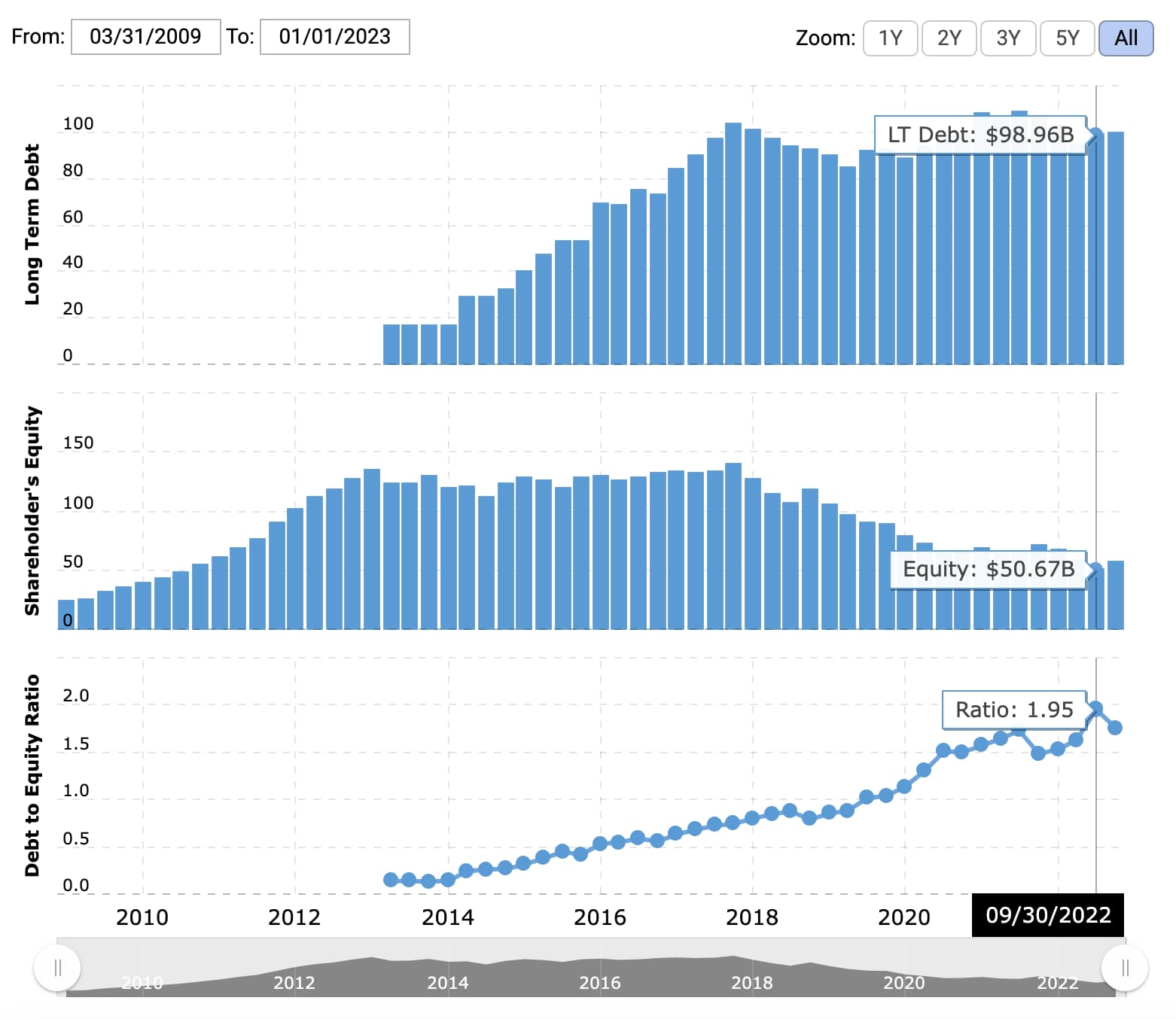
This figure means that for every dollar in equity, Restoration Hardware has $3.73 in debt. As noted above, the numbers you'll need are located on a company's balance sheet. Determining whether a company's ratio is good or bad means considering other factors in conjunction with the ratio.
Loan Calculators
This in turn makes the company more attractive to investors and lenders, making it easier for the company to raise money when needed. However, a debt to equity ratio that is too low shows that the company is not taking advantage of debt, which means it is limiting its growth. Company B has $100,000 in debentures, long term liabilities worth $500,000 and $50,000 in short term liabilities.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- The quick ratio measures the capacity of a company to pay its current liabilities without the need to sell its inventory or acquire additional financing.
- Sometimes preferred stock is considered an asset, while other times, it’s considered a liability.
- Perhaps 53.6% isn't so bad after all when you consider that the industry average was about 75%.
- This is because the company must pay back the debt regardless of its financial performance.
- A company's management will, therefore, try to aim for a debt load that is compatible with a favorable D/E ratio in order to function without worrying about defaulting on its bonds or loans.
- Debt-to-equity and debt-to-asset ratios are used to measure a company's risk profile.
For example, preferred stock is sometimes included as equity, but it has certain properties that can also make it seem a lot like debt. Specifically, preferred stock with dividend payment included as part of the stock agreement can cause the stock to take on some characteristics of debt, since the company has to pay dividends in the future. A debt-to-equity-ratio that’s high compared to others in a company’s given industry may indicate that that company is overleveraged and in a precarious position. Companies that don’t need a lot of debt to operate may have debt-to-equity ratios below 1.0.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
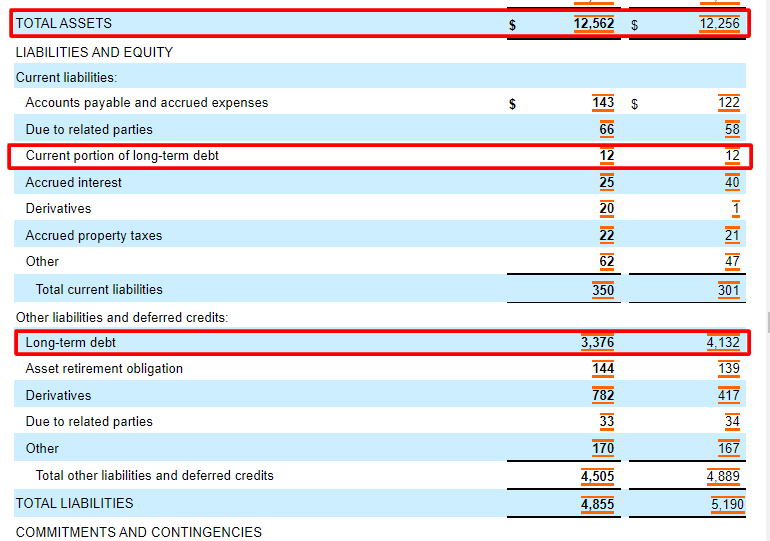
Total liabilities are all of the debts the company owes to any outside entity. On the other hand, a comparatively low D/E ratio may indicate that the company is not taking full advantage of the growth that can be accessed via debt. Simply put, the higher the D/E ratio, the more a company relies on debt to sustain itself. Liabilities are items or money the company owes, such as mortgages, loans, etc.
Formula
It is a problematic measure of leverage, because an increase in non-financial liabilities reduces this ratio.[3] Nevertheless, it is in common use. Banks often have high D/E ratios because they borrow capital, which they loan to customers. However, in this situation, the company is not putting all that cash to work. Investors may become dissatisfied with the lack of investment or they may demand a share of that cash in the form of dividend payments. At first glance, this may seem good — after all, the company does not need to worry about paying creditors. Like the D/E ratio, all other gearing ratios must be examined in the context of the company's industry and competitors.
Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. From Year 1 to Year 5, the D/E ratio increases each year until reaching 1.0x in the final projection period.
The current ratio reveals how a company can maximize its current assets on the balance sheet to satisfy its current debts and other financial obligations. The D/E ratio of a company can be calculated by dividing its total liabilities by its total shareholder equity. Other definitions of debt to equity may not respect this accounting identity, and should be carefully compared. Generally speaking, 3 steps to create a hiring process to identify the best candidates a high ratio may indicate that the company is much resourced with (outside) borrowing as compared to funding from shareholders. When used to calculate a company's financial leverage, the debt usually includes only the Long Term Debt (LTD). The composition of equity and debt and its influence on the value of the firm is much debated and also described in the Modigliani–Miller theorem.
If preferred stock appears on the debt side of the equation, a company’s debt-to-equity ratio may look riskier. Banks and other lenders keep tabs on what healthy debt-to-equity ratios look like in a given industry. A debt-to-equity ratio that seems too high, especially compared to a company’s peers, might signal to potential lenders that the company isn’t in a good position to repay the debt. The interest rates on business loans can be relatively low, and are tax deductible. That makes debt an attractive way to fund business, especially compared to the potential returns from the stock market, which can be volatile.
